Access powerful & easy-to-use numerical models
Book a software demoMaris Model Software Modules
Wave Propagation & Trasformation
The prediction of wave propagation and transformation in the nearshore is of paramount importance to design efficient coastal protection works and optimize the design of port layouts
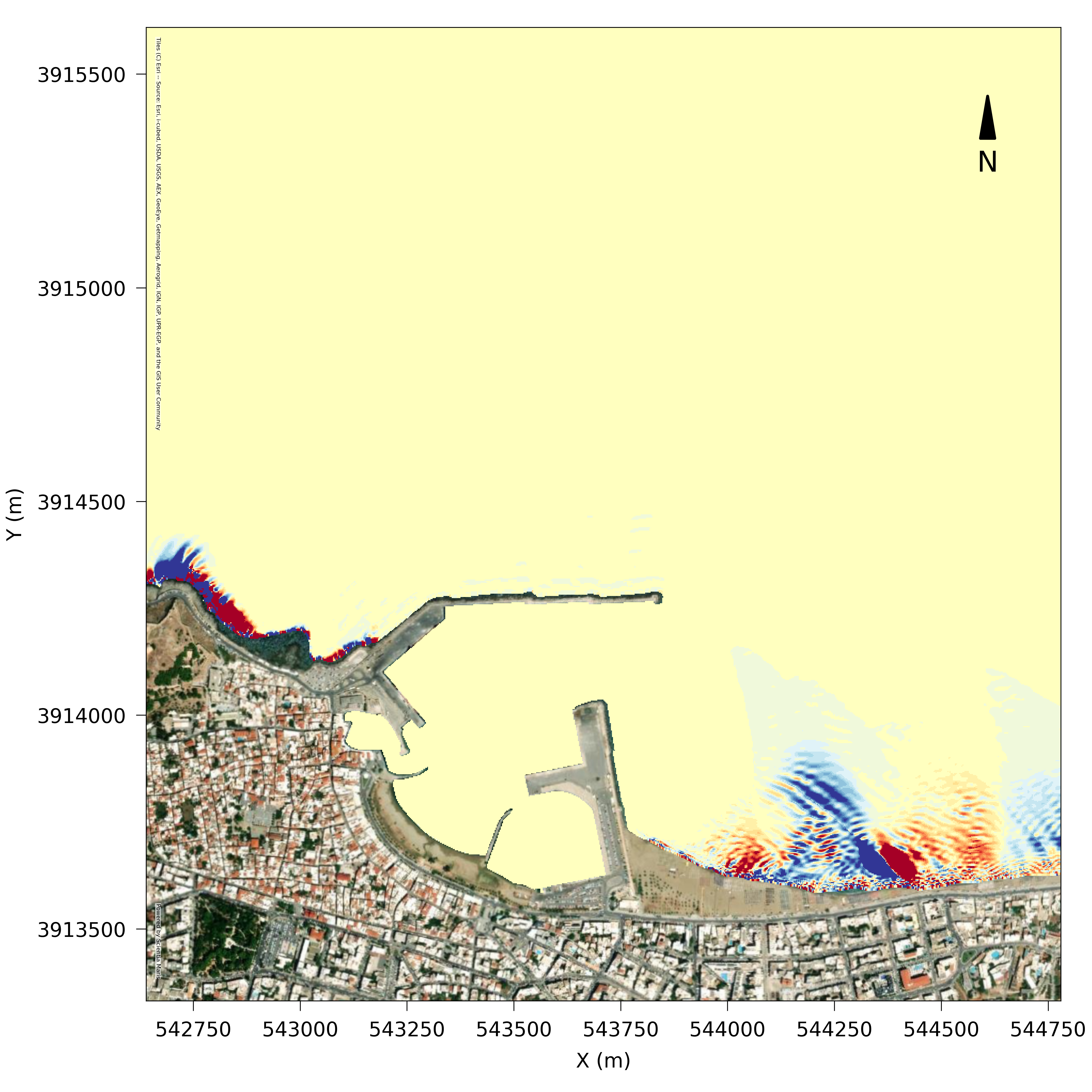
MARIS PMS Parabolic Mild Slope
Numerical model simulating wave propagation in open coastal areas
Maris PMS simulates irregular wave propagation, refraction, diffraction, and wave energy dissipation due to depth-induced breaking and bottom friction. It can be implemented for coastal impact studies
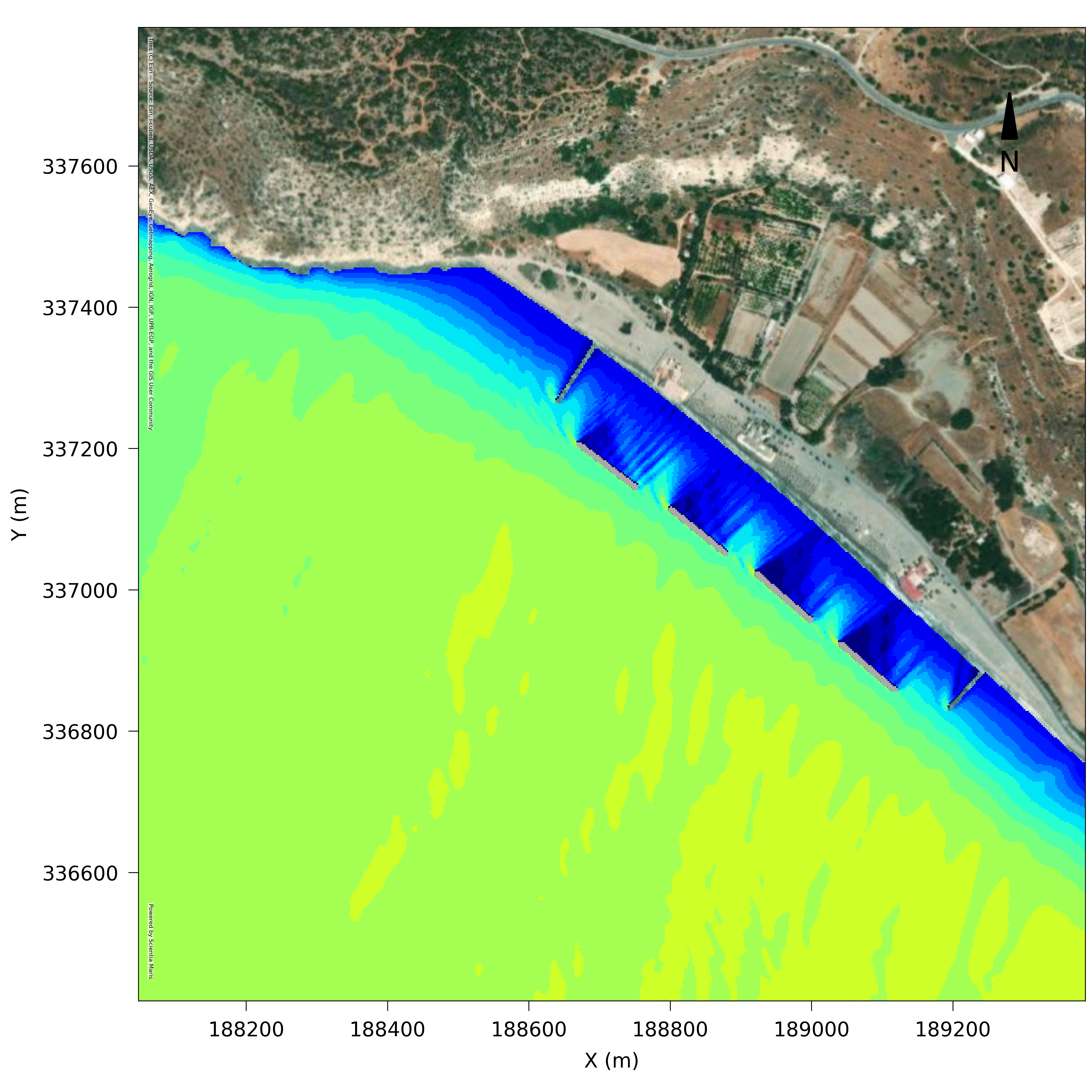
MARIS HMS Hyperbolic Mild Slope
Numerical model simulating wave propagation
Maris HMS is an advanced model capable of simulating multidirectional irregular wave propagation, refraction, reflection, diffraction, depth-induced breaking and bottom friction. It can be implemented for wave disturbance studies in ports, harbours and coastal areas as well as coastal impact studies to assess the effect of wave reflection & diffraction on the adjacent shores
Coastal Hydrodynamic Fields
Nearshore coastal hydrodynamic fields are generated by various forcing parameters (e.g. tide, wind, waves) and are vital for nearshore circulation and water renewal and the main cause for the transport of sediments in the shallow water
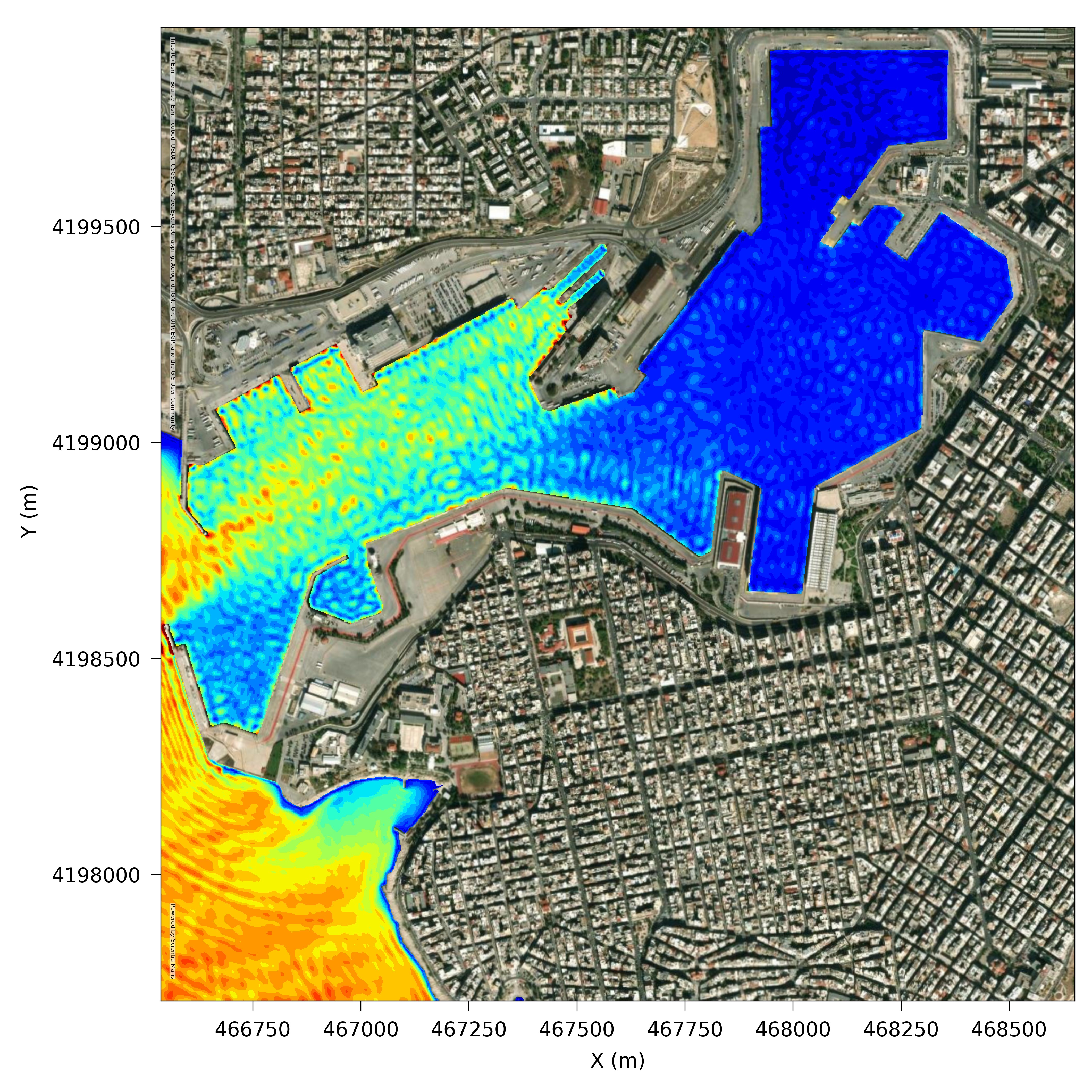
MARIS HYD Hydrodynamic model
Numerical model simulating coastal hydrodynamic fields
Maris HYD simulates water circulation in coastal areas in response to a variety of forcing functions. It can be implemented to calculate spatial and temporal development of wind and wave generated currents. It can be implemented for coastal impact & water renewal studies
Sediment transport & Sea Bed level change
The prediction of sediment transport & Sea Bed Level Change due to the combined effect of waves and currents is vital for identifying and mitigating potential erosion areas in coastal domains
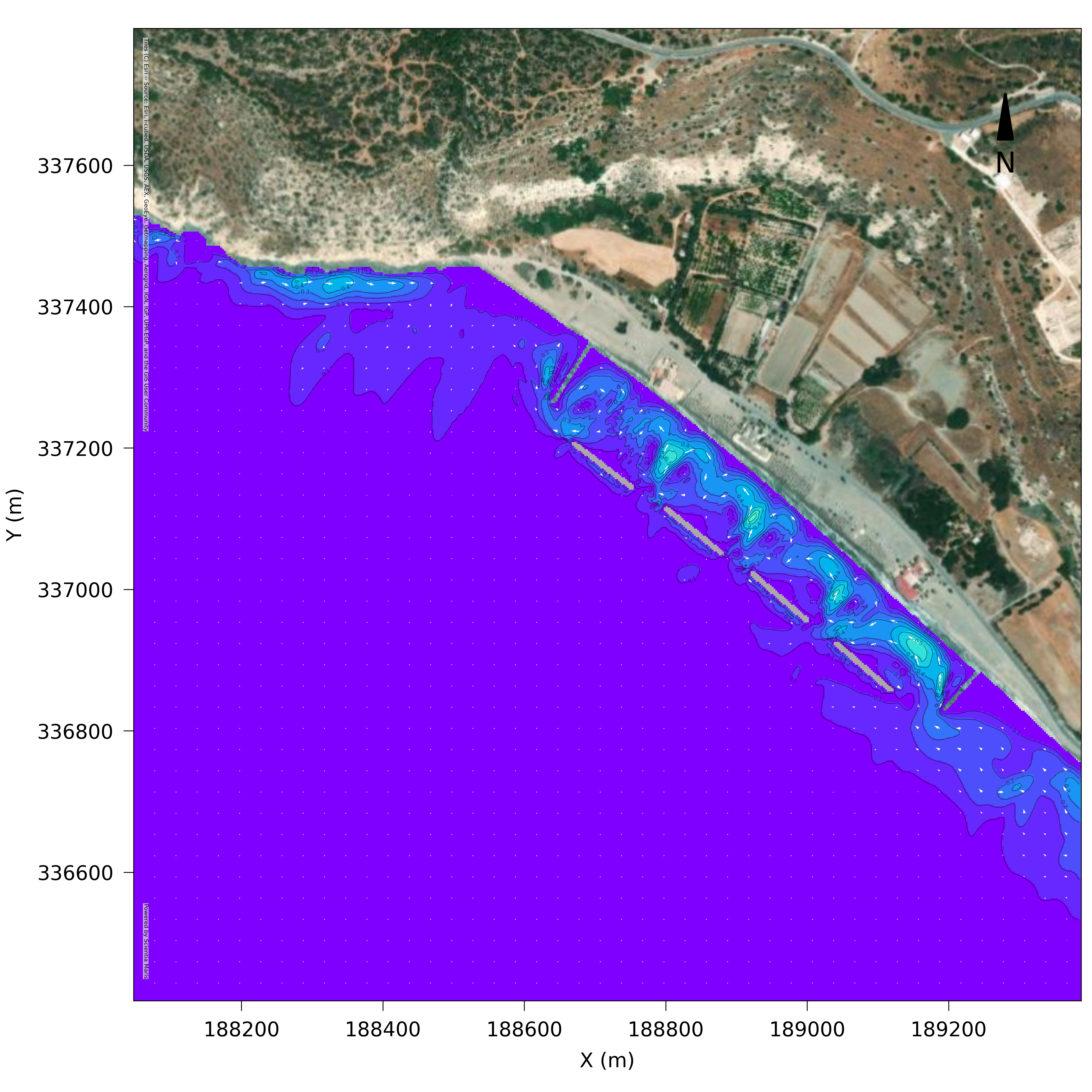
MARIS SDT Sediment Transport
Numerical model simulating bed evolution
Maris SDT model calculates sediment transport rates by taking into account current and wave action. It can be used to estimate rates of bed level changes, determining erosion and accretion areas. It can be implemented for coastal impact studies